You work out hard. As a result, you experience muscle pain, soreness, and fatigue. Before your next workout, those muscles need to recover. That's where magnesium comes in. This unassuming mineral may just hold the key to alleviating muscle soreness and muscle strain and boosting workout recovery.
In this article, we explore magnesium's ability to help reduce muscle pain so you can decide whether you need to add it to your supplement regimen. Here's what we'll cover:
- What Is Magnesium?
- Magnesium For Muscle Pain
- Other Benefits Of Magnesium
- Foods Containing Magnesium
- The Best Magnesium For Muscle Pain And Workout Recovery
- FAQs
What Is Magnesium?
The mineral magnesium is vital for many biochemical reactions inside the human body (1). One of nutrition's hidden heroes, it works in the background to support our health and wellbeing. Magnesium is readily available in the foods we eat and is also available as a supplement.
Magnesium is involved in more than 300 enzymatic processes, including regulating muscle contraction, energy production, nerve signaling, cardiovascular health, and bone strength. It has also shown itself to be able to reduce muscle soreness, enhance sleep quality, and boost post-workout recovery.
You can find out more about magnesium for sore muscles in the 7 Best Electrolyte Supplements To Fuel Your Workout.
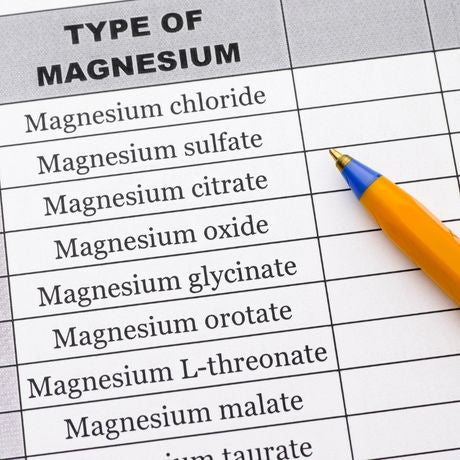
Types Of Magnesium Supplements
Magnesium supplements come in a variety of forms, each with particular qualities and possible health advantages. Here, we'll concentrate on the kinds of magnesium supplements frequently consumed, but we'll also touch on other forms, such as bath salts and topical applications:
- Magnesium Citrate: This type of magnesium is very absorbable and frequently used to enhance digestive health. It is often consumed as a supplement to encourage regular bowel movements because of its mild laxative effects.
- Magnesium Glycinate: This mild and easily absorbed type of magnesium is less likely to upset the stomach. People who want to promote sleep and relaxation frequently choose it for its calming effects.
- Magnesium Oxide: Although less accessible than certain other forms, magnesium oxide is frequently used as an antacid to treat heartburn. It might also be present in some multivitamin pills.
- Magnesium Malate: This type of magnesium is linked to malic acid. This combination can enhance the creation of energy. People who want to reduce fatigue and enhance workout performance frequently choose it.
- Magnesium L-Threonate: This more recent form of magnesium has drawn interest due to its ability to promote mental health and cognition. It is thought to have superior capacities to penetrate the brain.
- Magnesium Sulfate: You may be more familiar with magnesium sulfate as Epsom salt. It's frequently used in baths to soothe tight muscles and calm them.
- Magnesium Aspartate: Aspartic acid is blended with magnesium to form magnesium aspartate. This combination is believed to more effectively boost muscle function.
- Magnesium Chloride: A blend of magnesium and chlorine, this compound is an easily absorbable salt used to increase levels of magnesium in the body for things like blood pressure control and diabetes.
- Magnesium Carbonate: Usually used as an antacid, magnesium carbonate can assist in balancing stomach acid. As an oral supplement, it is less popular.
- Magnesium Taurate: Taurine and magnesium are combined to create magnesium taurate. It is occasionally chosen for its potential cardiovascular advantages.
- Magnesium Orotate: Magnesium orotate is a supplement that contains magnesium and orotic acid and is thought to promote cardiovascular health and athletic performance.
Magnesium For Muscle Pain
In this section, we go deep into the specifics to learn how magnesium for muscle pains can boost performance, help relieve delayed onset muscle soreness, and boost your workout recovery.
How Does Magnesium Help Sore Muscles?
Magnesium's ability to bring relief to your aching muscles comes from a combination of the following factors:
- Muscle Relaxation: An essential function of magnesium is to act as a muscle relaxant. It achieves this by controlling calcium ions, which are vital for muscle contractions. By preventing excessive calcium build-up in muscle cells, magnesium promotes greater relaxation.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Muscle discomfort is frequently caused by inflammation. Magnesium possesses anti-inflammatory qualities that can aid in reducing the discomfort and swelling brought on by achy muscles. As a result, magnesium helps the body recuperate by reducing inflammatory reactions.
- Better Blood Flow: Magnesium helps maintain healthy blood flow, ensuring muscles get enough oxygen and nutrients. By removing waste from muscular tissues, the improved circulation aids in accelerating recovery and reducing discomfort.
- Electrolyte Balance: Magnesium is one of the electrolytes that must be properly balanced for muscles to operate correctly. When you work out, magnesium can be lost through sweat. Magnesium replenishment aids in maintaining this equilibrium and guards against cramps and muscle tightness.
- Nerve Activity: Nerve irritation frequently causes muscle soreness. Magnesium helps to lower neural excitability and is essential for proper nerve function. Magnesium can reduce pain and discomfort by calming the nervous system.
- Replenishing ATP: Magnesium is needed to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the muscle's energy currency. With greater energy, muscles can recover faster.
- Better Sleep: Rest is essential for the rehabilitation of muscles. Magnesium is known for relaxing the nervous system and encouraging sound sleep. Your muscles can mend and regenerate themselves more efficiently with plenty of sleep.
A 2022 study looked at the effect of magnesium supplementation on muscle soreness and performance among college-aged male and female subjects. The magnesium group took 350 mg of magnesium per day for ten days. Compared to a placebo group, the magnesium group had significantly reduced delayed onset muscle soreness, as well as a reduced rate of perceived exertion and improved perceived recovery (2).
How Long Does Magnesium Take To Work For Muscle Pain?
The length of time it takes for magnesium to bring muscle relief can vary quite a bit between individuals. Here are the key factors that affect it:
- Form: The form of magnesium you take can affect how quickly it acts. While some types, such as magnesium citrate, are rapidly absorbed and may offer relief very quickly, others, such as magnesium oxide, are less accessible and may take longer to work.
- Dosage: The magnesium dose you take is important. Higher doses could offer more speedy relief, but adhering to suggested daily limits is critical because too much magnesium can cause stomach discomfort.
- Individual Variation: How each person's body responds to supplements varies. While some people can feel better in hours, others might need a few days to detect a difference.
- Muscle Pain Intensity: Muscle soreness or pain intensity also has an impact. Magnesium supplements may work faster to relieve mild discomfort than on more serious muscular aches or injuries.
- Consistency: Consistency is crucial while taking magnesium supplements. Magnesium levels in your body could take some time to balance out. Thus, regular supplementation can lead to improved outcomes over time.
- General Health: The rate magnesium acts depends on your general health. It can take longer to feel better if underlying medical issues prevent magnesium from being absorbed or used properly.
- Diet: Your diet and hydration level can affect how much magnesium is absorbed. Supplementation may be complemented with foods that contain magnesium. Keeping hydrated is also necessary for magnesium to function at its best.
- Stress & Sleep: Stress management and enough sleep both help magnesium work more effectively. Addressing these issues can lead to quicker treatment because prolonged stress and lack of sleep can increase muscle pain.
Although most people start to feel some relief from their muscle pain, remember that magnesium is not a magic bullet for severe pain or recent muscular injuries. A healthcare expert should be consulted for a thorough treatment plan if you have a specific muscle injury.

Does Magnesium Help With Muscle Cramps?
Magnesium has gained acceptance as a viable natural treatment for easing muscle cramps, and research suggests that it may be helpful in some circumstances.
To start, magnesium is a crucial mineral for the health of muscles because it helps control how they contract. It does so by opposing calcium, which is necessary for muscular contraction. By preventing the excessive calcium build-up in muscle cells, magnesium helps reduce the risk of cramping.
Magnesium can be lost through heavy sweating or activity, which can cause imbalances and raise the possibility of cramping. As such, magnesium dietary supplements help reestablish the electrolyte equilibrium.
Overactive nerves can contribute to cramping in the muscles. Magnesium helps soothe nerves by preventing the production of neurotransmitters that might cause muscles to contract.
Finally, magnesium promotes healthy blood flow, ensuring muscles receive enough oxygen and nutrients. This improved circulation, especially after a workout, might lower the chance of cramping.
Most interestingly, there is some promising research regarding the use of magnesium for cramps. A 2014 study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that supplementing with magnesium reduced the incidence of leg cramping in elderly women (3).
Anecdotal evidence also supports the use of magnesium for muscle cramps. Here are a couple of comments from users on Reddit:
"I like taking 100-200 mg magnesium malate in the morning and 100-200 mg magnesium glycinate at night to dull muscle pain/cramps. Sometimes I'll use a topical spray at night if it's really bothering me. (source)"
"Hell yeah, magnesium has nearly completely eliminated my calf and foot cramps. I started taking 400-600mg/day back in early summer, and the only time I've had any since has been when I don't take mag for a week or so. It is definitely one of my favorite supplements because it has made a noticeable impact. I take the taurate and malate forms, but it seems everyone has their own preference. Definitely worth exploring the different types, most are pretty cheap besides threonate and magtein." (source)
It is important to note that magnesium deficiency is not the only cause of muscle cramps. They can also be caused by dehydration, excess effort, and specific medical disorders.

Is Magnesium Good For Muscle Recovery Post-Workout?
Yes, magnesium can definitely help with post-workout muscle recovery in more than one way:
- Calcium Control: After an intense workout, your muscles may become tight and worn out. By controlling calcium ions, which are necessary for muscular contractions, magnesium helps reduce muscle tension. This calming effect helps lessen muscle soreness and stiffness after exercise.
- Inflammation Reduction: Magnesium's anti-inflammatory qualities can help reduce inflammation brought on by exercise, promoting recovery after your workout.
- Energy Creation: Since it's also needed to create ATP, the energy source for muscle cells, it helps provide the extra energy needed for post-workout muscle fiber repair.
- Protein Synthesis: Magnesium is a vital element to turning DNA and RNA into proteins, which heals damaged cells and aids muscle repair, recovery, and increased muscle mass.
- Electrolyte Replenishment: Heavy exercise can also cause electrolyte losses through sweat, especially with low magnesium intake. Increasing magnesium levels after exercise aids in reestablishing electrolyte balance, reducing cramps, and preserving healthy muscle function.
- Enhanced Circulation: Magnesium promotes proper blood flow, efficiently delivering nutrients and oxygen to muscle tissues. Increased circulation helps remove metabolic waste products, lowering the possibility of delayed onset muscular soreness (DOMS) and speeding up the healing process.
- Sleep: Magnesium also helps relax the nervous system to promote quality sleep, which is an essential part of the recovery process.
Here's what Reddit users have to say about the effectiveness of magnesium post-workout:
"So, a friend of mine suggested Magnesium supplements, and for me, it has been an absolute game changer when it comes to helping with DOMS from exercising.
I found when I reached mid 20s all of a sudden even light exercise would cause my muscles to get super sore and stiff to the point where I'd avoid exercise for days to weeks after even a mild exercise session. I tried everything I could think of- stretching before and after, incorporating hot yoga, ice, warm bath with salts, self massage, bengay... they all helped a bit but I was usually left being even less motivated with painfully sore and stiff leg muscles (especially calves.)
After taking magnesium, I rarely, if ever, get DOMS, and it's a manageable amount." (source)
"Replenishing my electrolytes (magnesium, potassium, sodium) after a tough workout day definitely seems to help me bounce back better too. I usually take 300mg magnesium citrate, 1 tsp of potassium salt substitute and 1 tsp of kosher salt and mix it all up in a blender bottle with Mio and sip on it for a few hours. It definitely helps curb my fatigue and soreness after doing a 10k." (source)
How Much Magnesium Do You Need For Optimal Workout Recovery?
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium, as set by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States, is as follows:
- Adult Males (19-30 years): 400 milligrams (mg) per day
- Adult Males (31 years and older): 420 mg per day
- Adult Females (19-30 years): 310 mg per day
- Adult Females (31 years and older): 320 mg per day
Recommended dosages for athletes and active people are generally higher than those for sedentary people, in the 400-600 mg range daily. This is in line with the dosages used in clinical trials.

Other Benefits Of Magnesium
Magnesium has many other health advantages beyond helping with workout recovery. Here's a rundown:
- Improved Sleep: Magnesium has a calming effect on the central nervous system, which may help you fall asleep faster.
- Stress Reduction: Magnesium helps control neurotransmitters that affect mood. The symptoms of tension and anxiety may be reduced, and a feeling of relaxation may be encouraged by consuming enough magnesium.
- Heart Health: Magnesium helps maintain normal blood pressure levels and reduces the risk of heart arrhythmia.
- Bone Health: Supplementing with magnesium complements calcium and vitamin D in building strong bones.
- Digestive Tract Health: Magnesium helps keep the digestive tract's smooth muscles working smoothly.
- Control of Blood Sugar: People with diabetes or those at risk for developing the disease may benefit from magnesium supplementation for controlling their blood sugar levels.
Foods Containing Magnesium
The following foods are excellent sources of magnesium:
- Leafy green vegetables like kale, spinach, and collard greens
- Nuts such as almonds, peanuts and cashews
- Pumpkin, sesame, and flax seeds
- Whole greens like whole wheat, oats, quinoa and brown rice
- Avocado
- Legumes, such as chickpeas, beans, and lentils
- Bananas
- Dark chocolate
- Salmon and mackerel fish
- Bone broth
Learn more about the many health benefits of bone broth here.
The Best Magnesium For Muscle Pain And Workout Recovery
Magnesium is an excellent workout recovery aid. While you can get a decent amount from food, taking a daily supplement is the most efficient way to get a consistent and adequate dosage.
Our favorite magnesium supplement is Pure Encapsulations Magnesium Citrate. Each capsule contains 150 mg of magnesium citrate, one of the most bioavailable forms of magnesium. We recommend taking two capsules per day for a dosage of 300 mg.
Check our review of the 7 Best Magnesium Supplements on today's market.

Our supplements are made with only premium ingredients sourced from trusted suppliers and guided by our nutritional experts, then carefully manufactured and tested to verify their potency...
Other FAQs
Still have questions about magnesium for muscle pain? Here are the answers to four of the most common questions we get on the subject:
Is it better to take magnesium before or after my workout?
Whether you should take your magnesium either before or after an exercise depends on your goals. Magnesium supplements can improve hydration, energy generation, and muscle performance before exercise.
On the other hand, magnesium post-workout helps with muscle healing, replacing lost electrolytes, and encouraging better sleep. Consider splitting your magnesium intake up to reap the benefits of both, or speak with a healthcare professional for advice tailored to your needs and level of exercise.
Does magnesium help muscle injury?
Yes, magnesium can help muscles recover from injury. It promotes the healing of damaged tissue, eases inflammation, and helps muscles relax. Magnesium also aids in reducing muscle cramping and spasms, which are frequent in sore muscles.
Magnesium supplements should, however, complement other parts of injury management, such as rest, physical therapy, and correct nutrition, so it's crucial to speak with a healthcare professional for a whole treatment plan.
Is too much magnesium bad for your muscles?
Yes, consuming too much magnesium can harm muscles. Extremely high doses may result in exhaustion, muscular wasting, and, in severe cases, heart issues. Before taking high-dose magnesium supplements, see a healthcare provider to ensure you stay below safe limits and avoid any adverse effects on muscular function.
Who should not take magnesium?
Magnesium supplementation should be avoided by anyone with serious kidney issues, a history of allergies to magnesium supplements, or particular medical diseases such as myasthenia gravis.
Magnesium For Muscle Pain: Takeaways
Magnesium is crucial for promoting muscle health and recovery. Due to its anti-inflammatory characteristics, function in the creation of energy, and capacity to replace electrolytes, it helps to ease muscle aches, encourage relaxation, and speed up recovery after exercise. As such, it's a smart supplement to add to your workout program
Magnesium citrate from Pure Encapsulations is a standout choice for dietary supplements. It offers a straightforward approach to make sure you meet your daily magnesium needs with 150 mg of highly absorbable magnesium citrate per capsule.
Check out our review of the 7 Best Magnesium Supplements Of 2023 to learn more and grab some magnesium to start recovering better.

References
- Fiorentini D, Cappadone C, Farruggia G, Prata C. Magnesium: Biochemistry, Nutrition, Detection, and Social Impact of Diseases Linked to Its Deficiency. Nutrients. 2021 Mar 30;13(4):1136. doi: 10.3390/nu13041136. PMID: 33808247; PMCID: PMC8065437.
- Reno AM, Green M, Killen LG, O'Neal EK, Pritchett K, Hanson Z. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Muscle Soreness and Performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2022 Aug 1;36(8):2198-2203. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003827. Epub 2020 Oct 1. PMID: 33009349.
- Veronese N, Berton L, Carraro S, Bolzetta F, De Rui M, Perissinotto E, Toffanello ED, Bano G, Pizzato S, Miotto F, Coin A, Manzato E, Sergi G. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on physical performance in healthy elderly women involved in a weekly exercise program: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Sep;100(3):974-81. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.080168. Epub 2014 Jul 9. PMID: 25008857.

0 Comments